Are you aware of the testing required to ensure the quality of sterile products?
We frequently use eye drops, injectables, and other products that must meet the requirement of being sterile. How is this achieved? This characteristic is crucial for a pharmaceutical product and must be ensured through a properly designed and validated manufacturing process.

Sterility of a product is achieved by managing the bioburden and implementing appropriate aseptic techniques during processing. In this regard, the European Pharmacopoeia advises conducting a Sterility Test to confirm whether a product meets this standard.
So, how is a Sterility Test conducted?
Before performing the Sterility Test, several preliminary evaluations are necessary. The first is the Growth Promotion Test, which verifies that the culture media can support the growth of very low levels of microorganisms. This test also confirms the nutritional properties of each batch of media to be utilized.
To carry out this test, fewer than 100 CFU of each microorganism specified in the Ph. Eur. must be inoculated into Thioglycollate Fluid Medium (TFM) and Trypticasein Soy Broth (TSB), along with TSA/SDA serving as a positive control. If clear growth is observed after incubation, the medium is deemed suitable.
The second requirement is the Method Suitability Test, which is conducted concurrently with the Growth Promotion Test to ensure that the method is effective for controlling product sterility.
In this test, the same methods as the Sterility Test (membrane filtration or direct transfer) are utilized, but the product is transferred into each medium, TFM/TSB, and then inoculated with fewer than 100 CFU of each species.
After incubation, the test is considered suitable if visible growth is observed compared to a blank (without the product). If no growth is seen, this indicates that the product possesses antimicrobial activity.
As previously mentioned, the Sterility Test must be performed under aseptic conditions and can be done using either membrane filtration or direct transfer. The European Pharmacopoeia specifies the minimum and maximum volumes of the product to be tested, as well as the appropriate method, depending on the nature of the products.
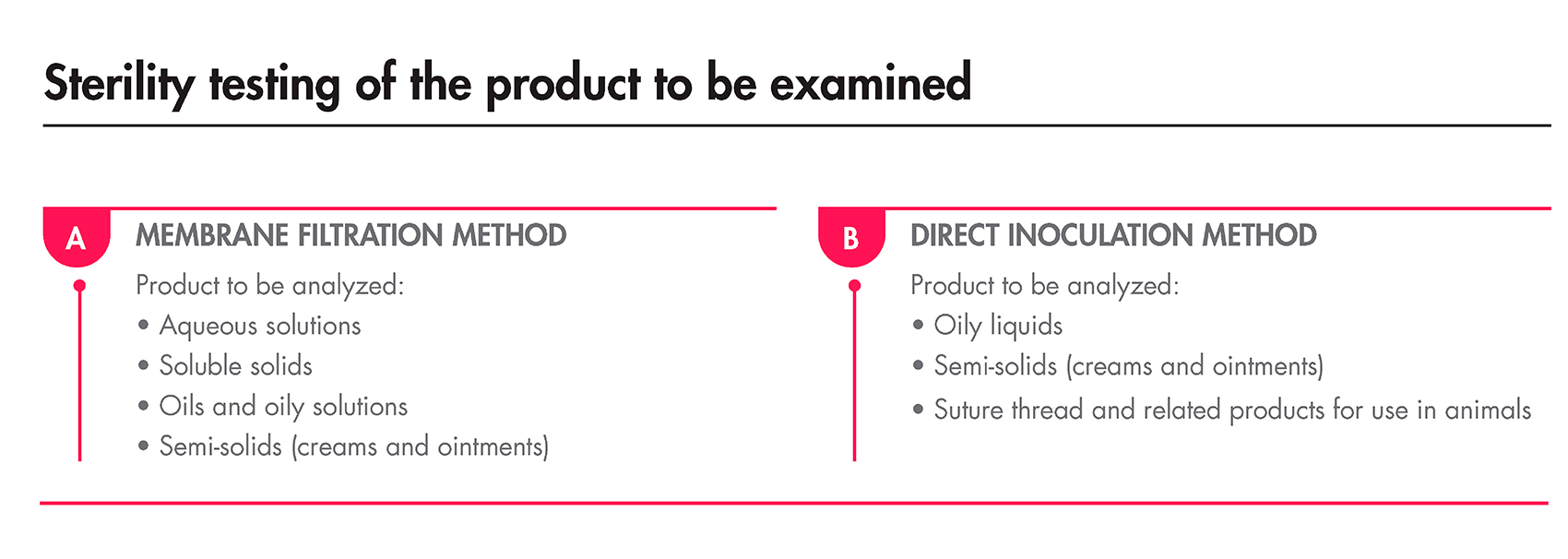
The incubation period, regardless of the method used, must last for 14 days. After this duration, if no turbidity is detected, the product is deemed compliant with the test.
Are only two culture media required?
Both TFM and TSB are general media with highly nutritious properties that support the growth of a wide range of bacteria (both aerobes and anaerobes) and fungi at very low levels. This is important because, under the principle of sterility, a significant number of microorganisms that could contaminate the product should not be present.
Additionally, this method is harmonized with the USP and JP, which adds a significant advantage.
At Asiagel, we offer media that align with pharmacopoeial standards for performing the Sterility Test without any complications. Each batch is evaluated to ensure compliance with high-quality standards, guaranteeing their sterility and effectiveness.



